Tomorrow and tomorrow and tomorrow
Creeps in this petty pace from day to day
To the last syllable of recorded time,
And all our yesterdays have lighted fools
The way to dusty death. Out, out, brief candle!
Life’s but a walking shadow, a poor player
That struts and frets his hour upon the stage
And then is heard no more. It is a tale
Told by an idiot, full of sound and fury,
Signifying nothing.
Macbeth, Act V, Scene V by William Shakespeare
The IPL 2026 carnival is just around the corner, and my enhanced IPL app “IPL AI Oracle” is just in time for IPL fans. The current version of IPL AI Oracle, refines my earlier implementation to be more accurate and to handle a wider range of natural language queries related to IPL. My previous post “Introducing IPL AI Oracle: AI that speaks cricket!!! discusses an implementation which had 4 tabs
- General queries
- Match Analysis
- Head-to-head
- Team vs All Teams
The data for this app comes from Cricsheet. The data consists of ball-by-ball data for all IPL matches since 2006 in yaml format. This data was then pre-processed into a suitable format for use by the tabs both for the analytics and the natural language query functionality
The tabs provide analytics of IPL matches, head-to-head and team vs All Teams. Each of the 4 tabs allow for user query in natural language based on the tab general queries, queries on IPL matches, queries on head-to-head performance between 2 teams and natural language queries between a team versus All Teams.
For details about the implementation, please see the post “Introducing IPL AI Oracle: AI that speaks cricket!!! The IPL analytics are based on my Python package ‘yorkpy‘. which itself is based on its earlier avatar ‘yorkr‘ in R available in CRAN. For handling the natural language queries, in my previous implementaion, I used prompt templates for each of the tabs which would construct an appropriate prompt to gpt-4.1-nano LLM. Ths earlier implementation with prompt templates worked fine for a reasonable number of user queries. However, for each user query the prompt constructed was quite large and guzzled up tokens quite fast and I was running out of my subscription very early.
So, in this current implementation I finetune gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18, one of the smaller gpt models, to keep the costs low. The prompt templates were reduced to the bare minimum. The gpt-40-mini-2024-17-18 model is then trained on hand-created individual training examples for each tab. The initial set of training examples was around 220 queries with corresponding pandas code. The split is as follows
- matches: 65 rows
- head_to_head: 50 rows
- teamVsAllTeams: 48 rows
- general_queries: 39 rows
This is the ground truth from which all other examples were created. Subsequently, I used Claude Sonnet 4.5 to augment the initial set of questions. The amplification essentially consisted of different ways of asking the same query for example
- What is V Kohli’s strike rate in IPL?
- Show me V Kohli’s strike rate
- V Kohli’s strike rate
- Display V Kohli’s strike rate etc
- Can you tell me V Kohli’s Strike rate
- Find V Kohli’s Strike rate
- …
The augmented data set was used in finetuning. The finetuning process was done several times as I would take each finetuned model and test it manually. I would find issues. Sometimes the question pattern itself would be missing or it would generate incorrect response Fortunately Sonnet 4.5 helped me to identify patterns which were under-represented or were inconsistent with other queries with similar patterns. Additional training examples were added for complex queries which required the generation of a lot of code for e.g. the batting or bowling scorecard in matches, head_to_head or teamAllTeams
The original training examples are augmented to produce 2760 examples with 12 variations for simple patterns and 15 training examples for complex ones. The scorecard code is further boosted and the final number of training examples are 3831 training data which cannbe split into
- matches: 1212 examples
- head_to_head: 1032 examples
- teamVsAllTeams: 1002 examples
- general_queries: 585 examples
This training data is then shuffled and split into training and validation in the ratio of 3447 (90%) : 384 (10%).
The base model was gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18 which was the smallest and most economical. The default hyper parameters were used
- Epochs – 3
- Batch size – 6
- LR multiplier – 1.8
- Seed – 3
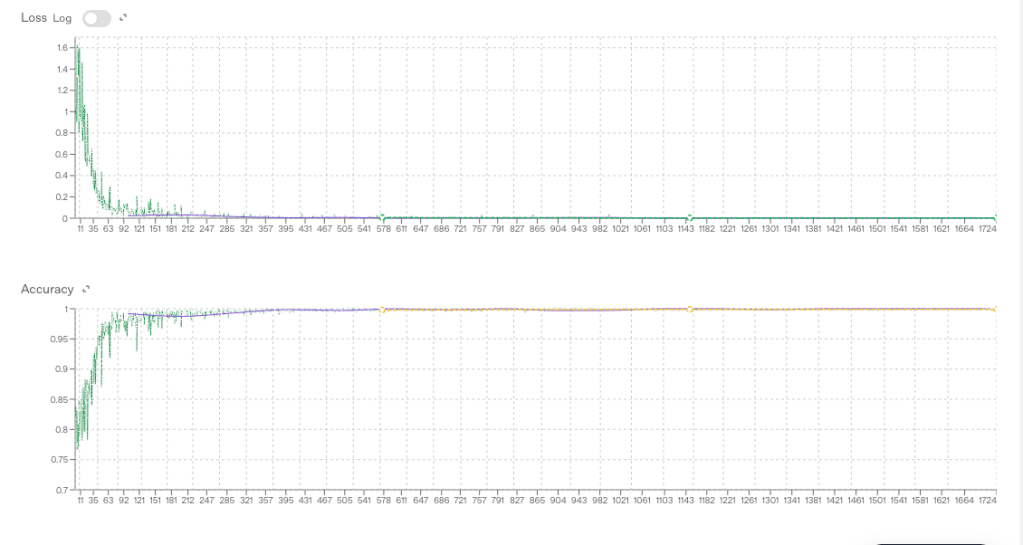
- Train loss – 0.000
- Validation loss – 0.003
- Full validation loss – 0.002
Try out the enhanced IPL AI Oracle – https://wizard-ai-three.vercel.app/
(When you click the above link, a page will open. Enter your email and click ‘Send magic link‘ button below. This will send a magic link to your email. Click the ‘Sign in’ button which will allow you login to the app IPL AI Oracle and start using it.)
Natural language queries
Here are some random natural language queries in different tabs
A) General queries tab
This tab deals with general on IPL queries
1) Top 3 scorers in IPL 2025?
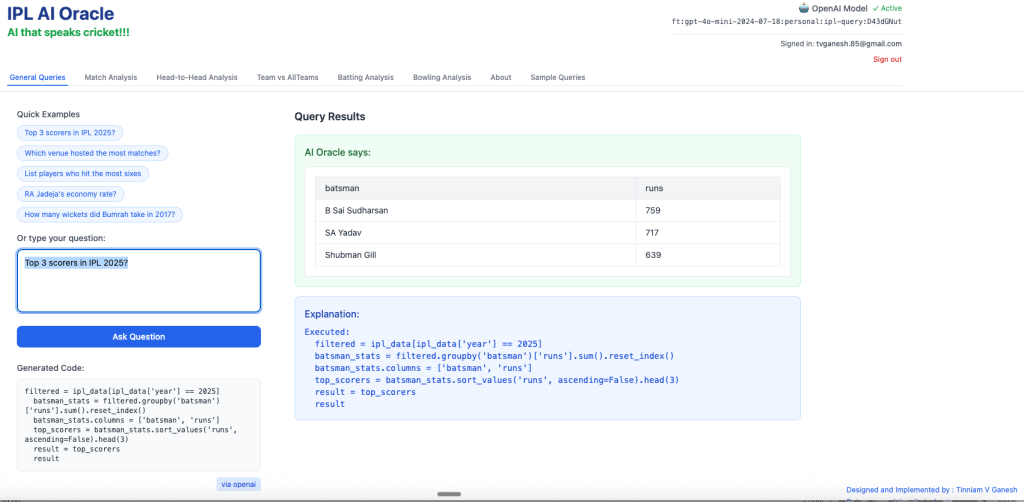
…
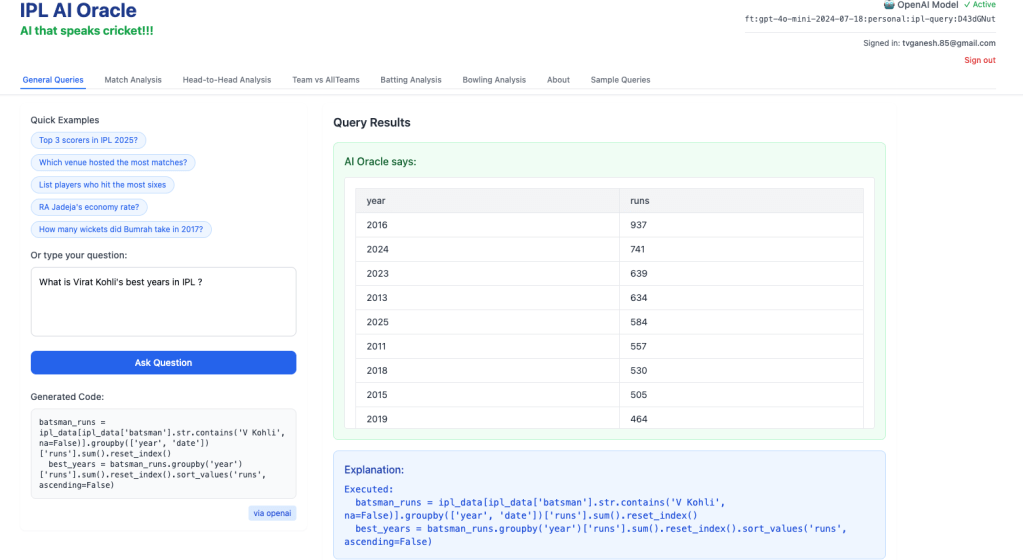
2) What is Virat Kohli’s best years in IPL?
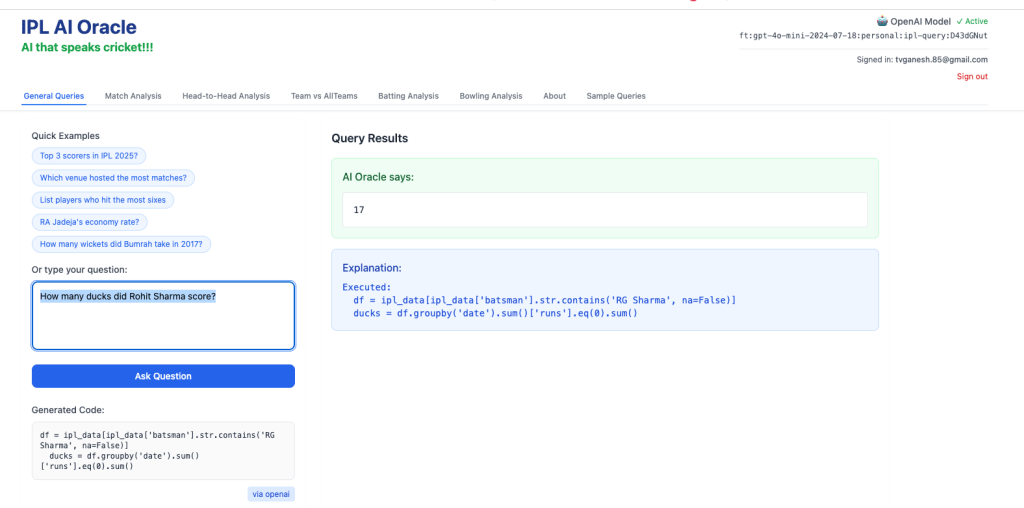
3) How many ducks did Rohit Sharma score in IPL?
4) What is Ravindra Jadeja’s Economy rate?
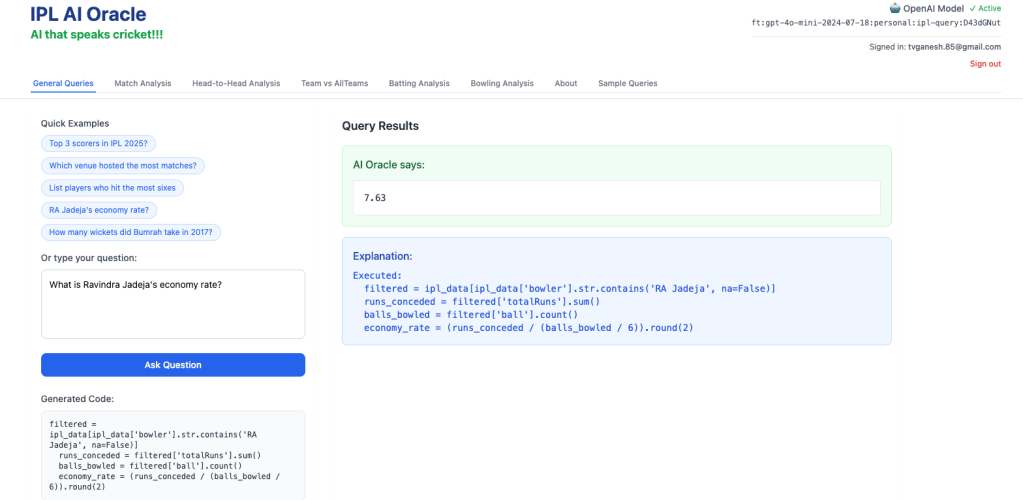
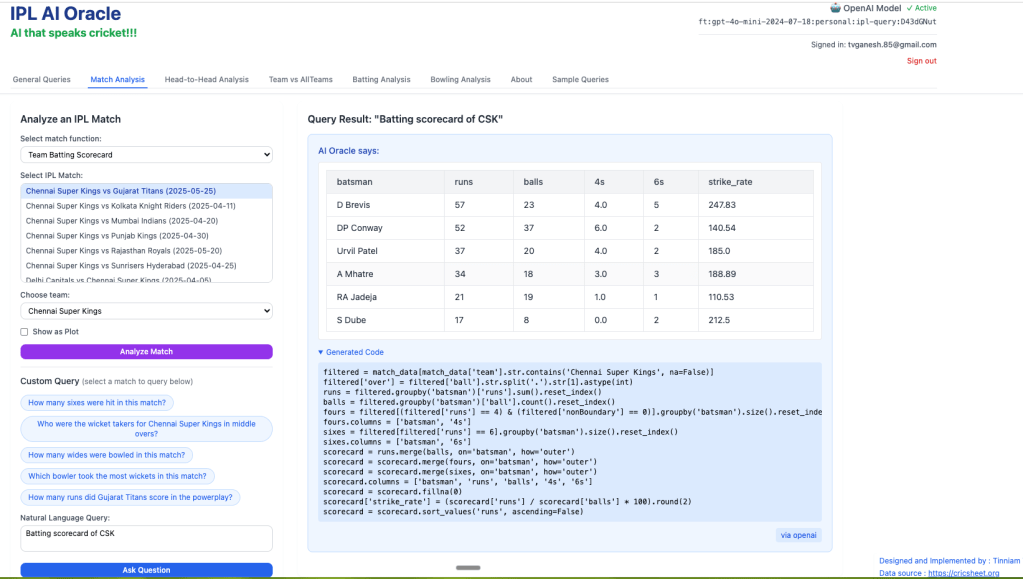
B) Matches tab
This tab deals with a selected individual match
- Batting scorecard of CSK
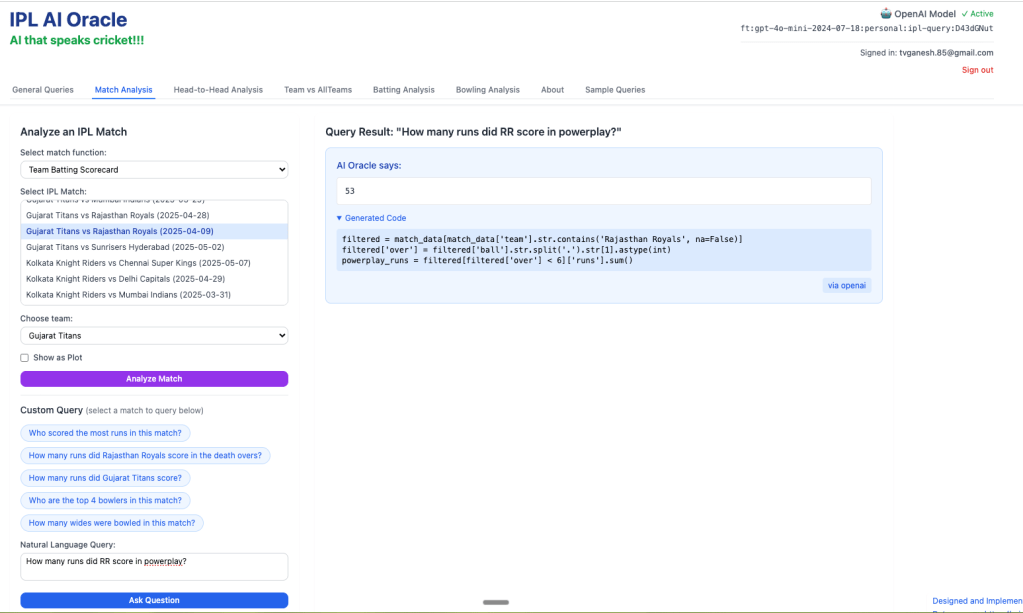
2) How many runs did RR score in powerplay?
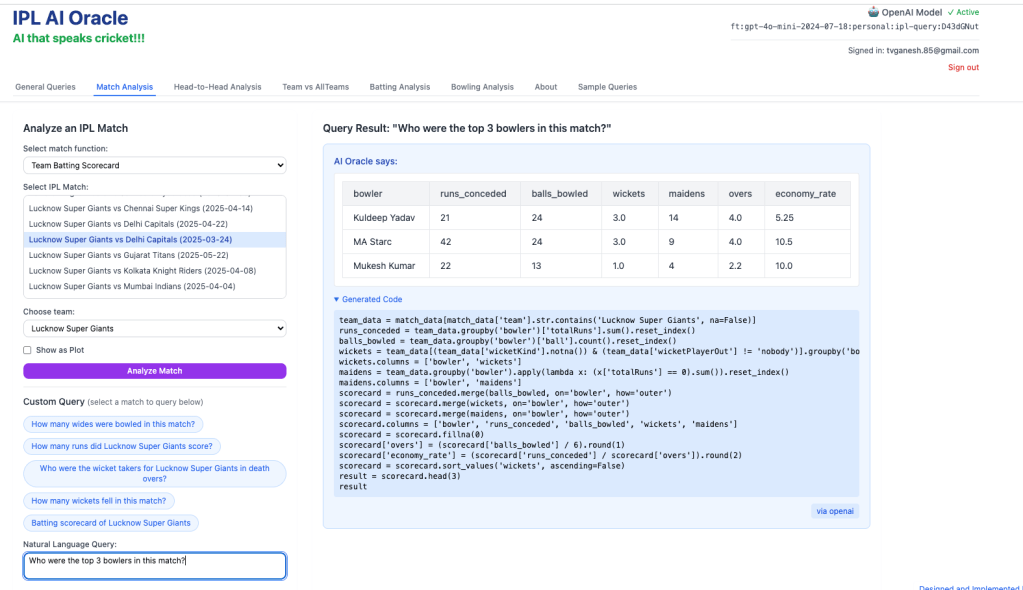
3) Who were the top 3 bowlers in this match?
4) Who took wickets for in middle overs for Delhi Capitals?
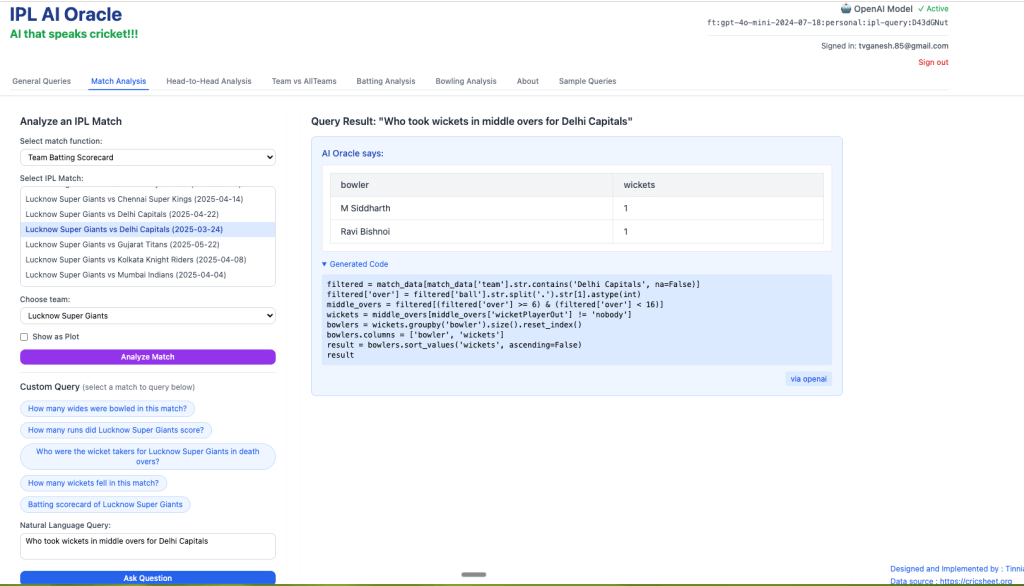
C) Head to head tab
This tab takes into consideration all matches played between the 2 selected teams
- Bowling scorecard of Delhi Capitals
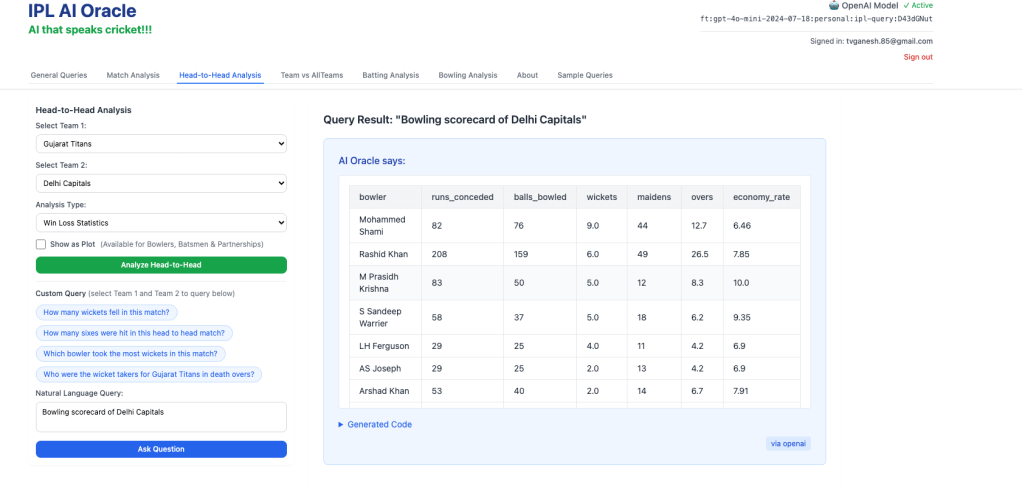
2. Who took the most wickers for KKR?
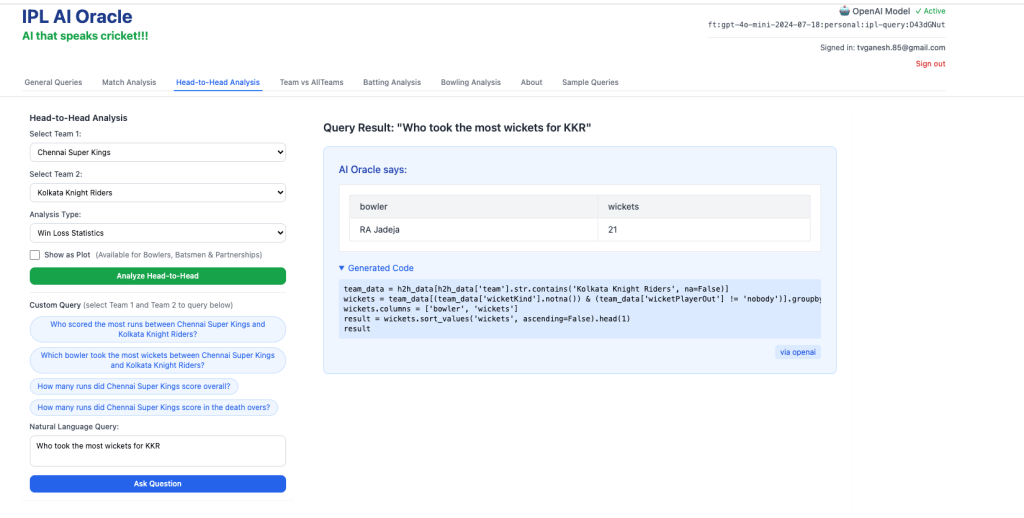
3) Who were the top scorers for KKR in death overs?
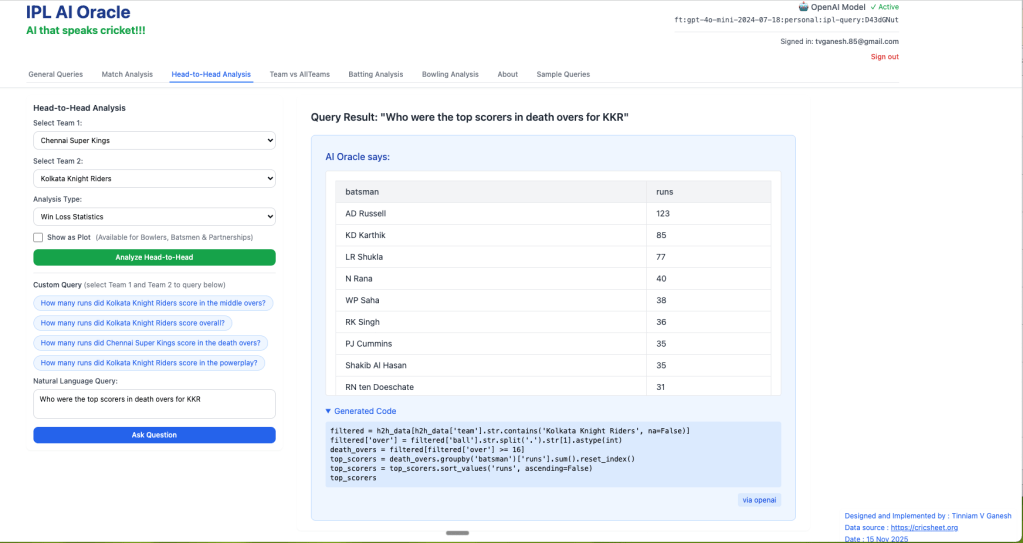
D) Team vs All Teams
- Who were most wicket takers for Chennai Super Kings in death over?
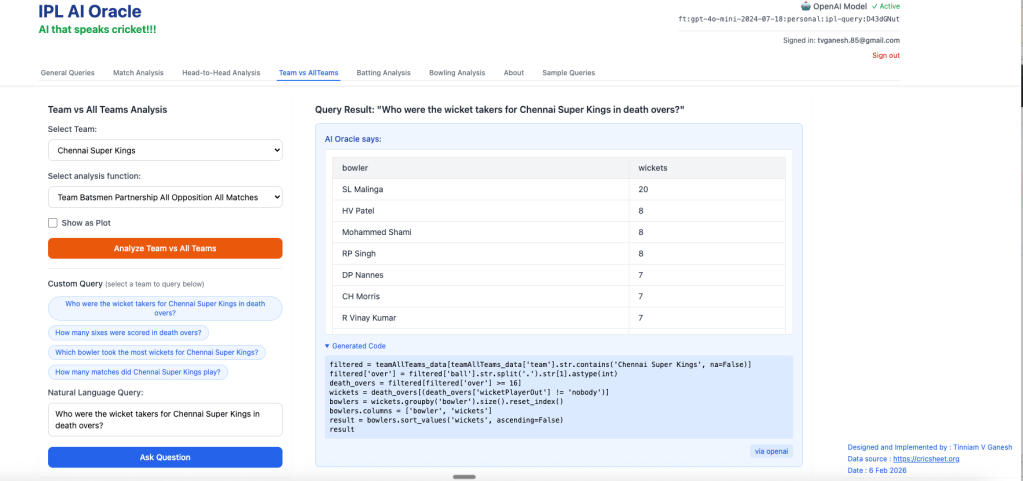
2. How many sixes did Dhoni hit in death overs?
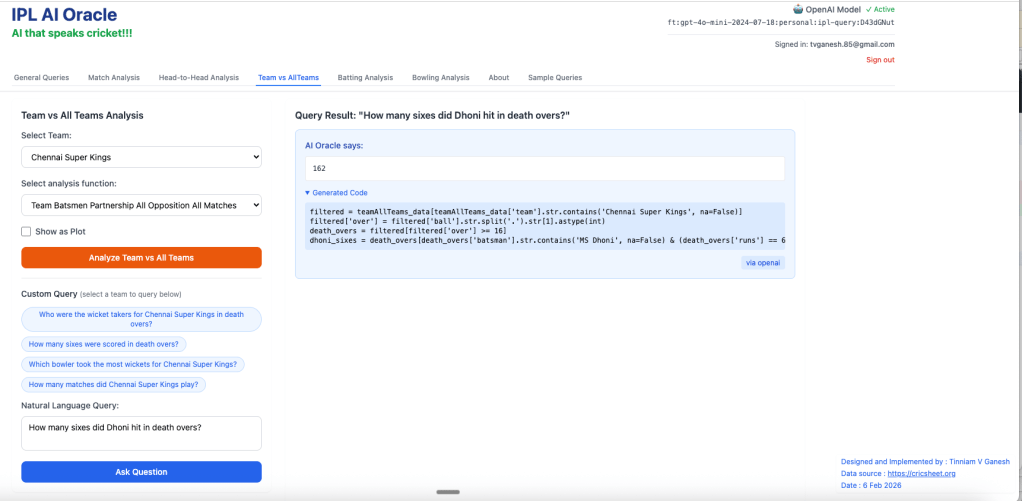
3. Which batsmen from Gujarat Titans scored more than 100 runs?
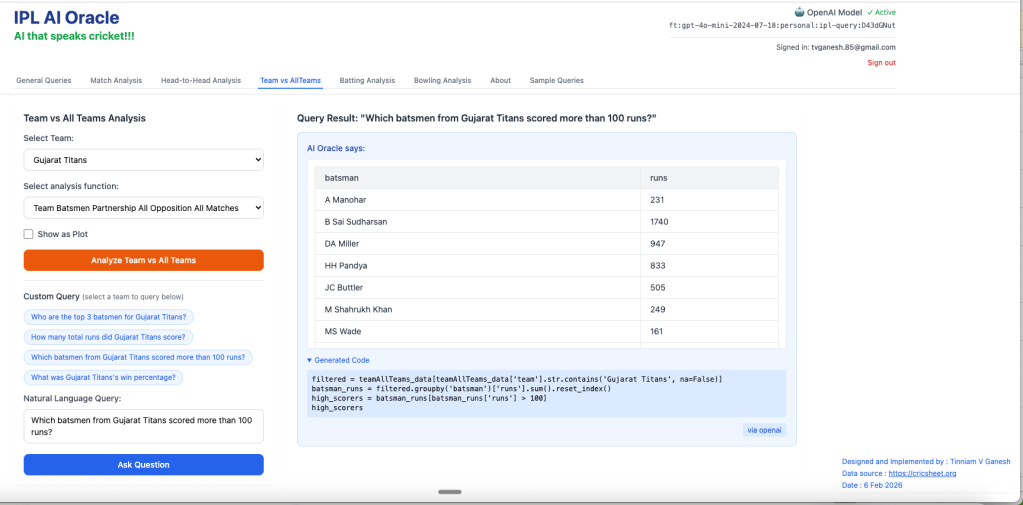
In addition I have added 2 other tabs to the earlier tabs. Now there is
- Batting Analysis tab
- Bowling Analysis tab
These tab provide various batting and bowling analytics for IPL players
E) Batting Analysis tab
- batsmansFoursSizes – AB De Villiers
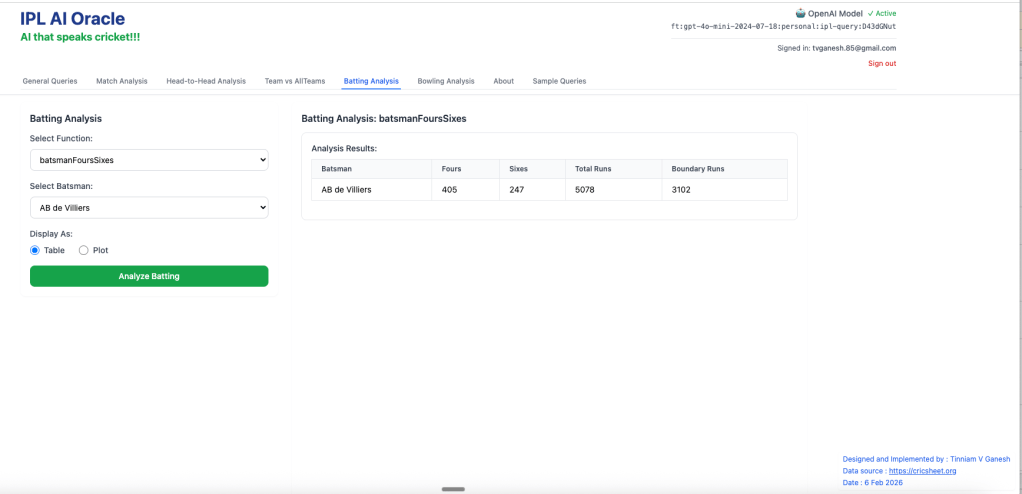
2. batsmanRunsVsStrikeRate – AB de Villiers
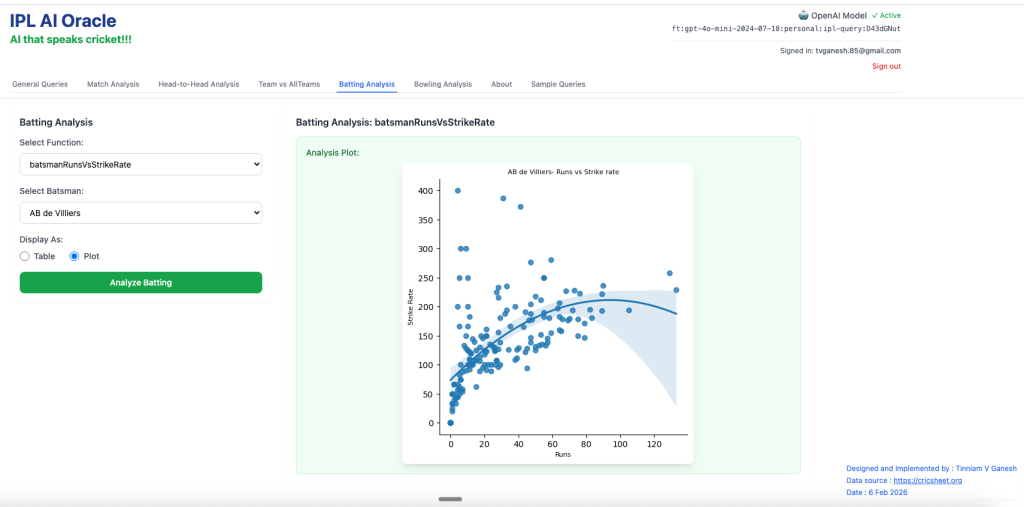
3. batsmanMovingAverage – Virat Kohli
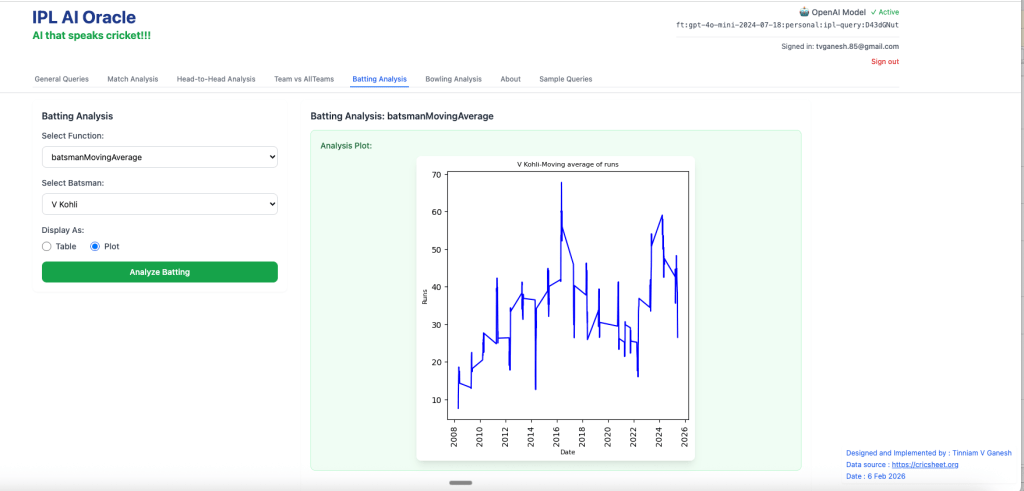
4. batsmanCumulativeStrikeRate – Chris Gayle
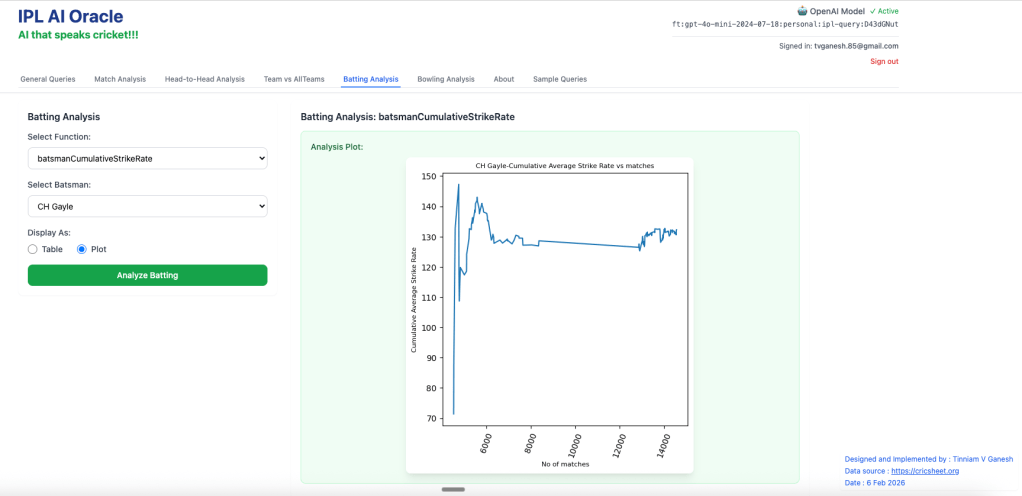
F) Bowling Analysis Tab
- bowlerMeanEconomyRate – Andre Russell
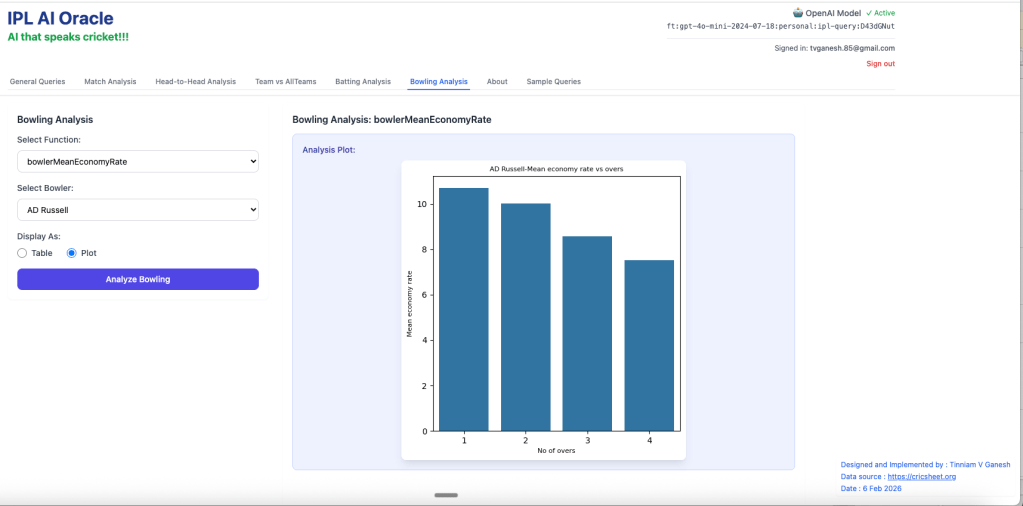
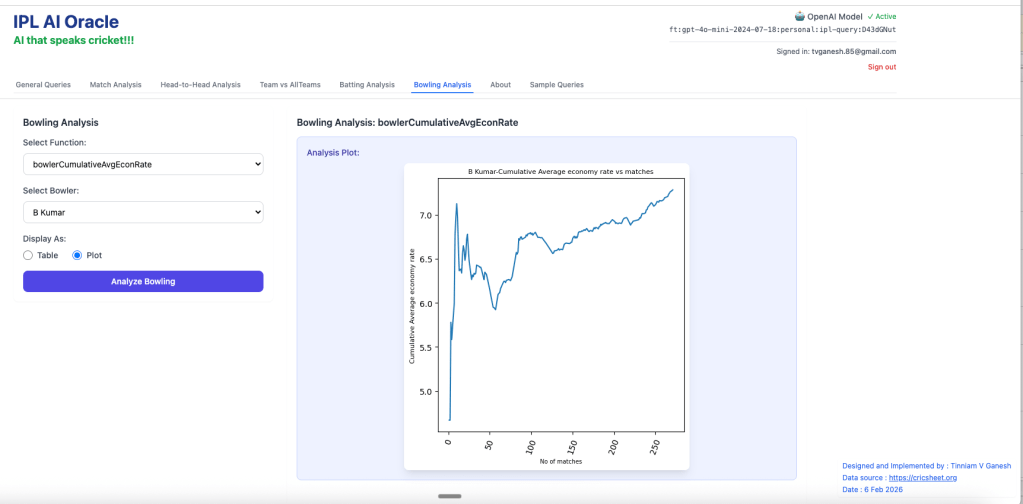
2. bowlerCumulativeAverageEconRate – Bhuvaneshwar Kumar
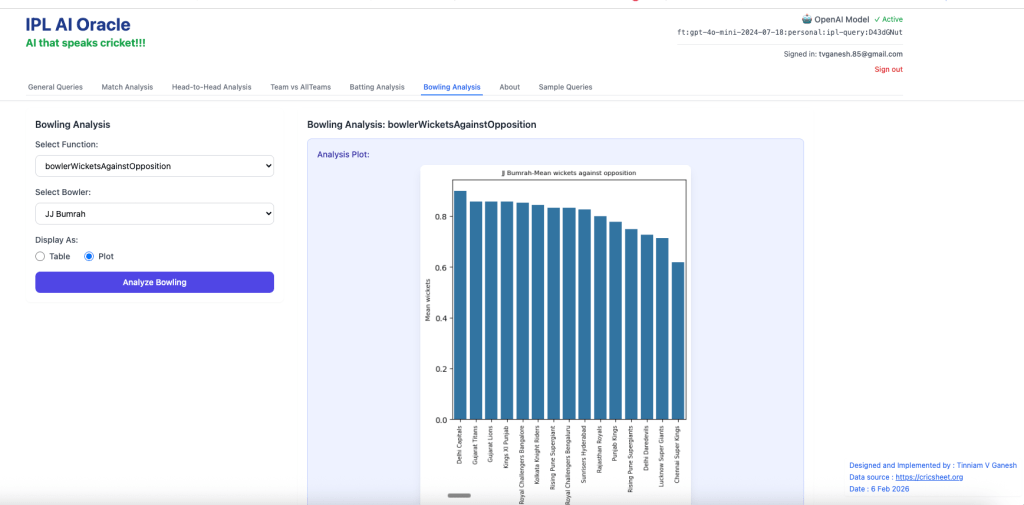
3. bowlerWicketsAgainstOpposition – Jasprit Bumrah
Try out the enhanced IPL AI Oracle – https://wizard-ai-three.vercel.app/. Enter your email and click the magic link sent to your email.
Note:
- IPL AI Oracle can make mistakes and sometimes generate erroneous code
- If the answer is wrong try to rephrase the question.
- Try to use the full name Rohit Sharma if possible
- You can use abbreviations like ER, SR and for teams CSK, RCB, KKR etc
- IPL AI Oracle is not always one shot, sometimes it is 2-shot
I will try to improve the model in future versions. For the current version I had to do some of the steps including the testing manually. I would like to experiment with Claude Code and automate the generation of training data, finetuning, testing using the finetuned model (using a test harness) and subsequently correcting/adding to the training data if needed repeating the steps again till the tests pass with a high degree of accuracy. Lets see.
Do give IPL AI Oracle (https://wizard-ai-three.vercel.app/) a try!!!
Also see
- Deblurring with OpenCV: Weiner filter reloaded
- Introducing QCSimulator: A 5-qubit quantum computing simulator in R
- Deconstructing Convolutional Neural Networks with Tensorflow and Keras
- Natural language processing: What would Shakespeare say?
- Presentation on “Intelligent Networks, CAMEL protocol, services & applications”
- Re-introducing cricketr! : An R package to analyze performances of cricketers
- Deep Learning from first principles in Python, R and Octave – Part 4
- The Anomaly
To see all posts click Index of posts
